Get Started with Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- February 10, 2023
- by
- Nawrin
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a technology that prevents sensitive or confidential information from leaking outside of an organization. DLP solutions typically work by identifying and classifying sensitive data, monitoring for data exfiltration attempts, and, if necessary, blocking or restricting access to sensitive data. DLP’s goal is to reduce the risk of data breaches, protect intellectual property, and ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), as well as PCI-DSS.
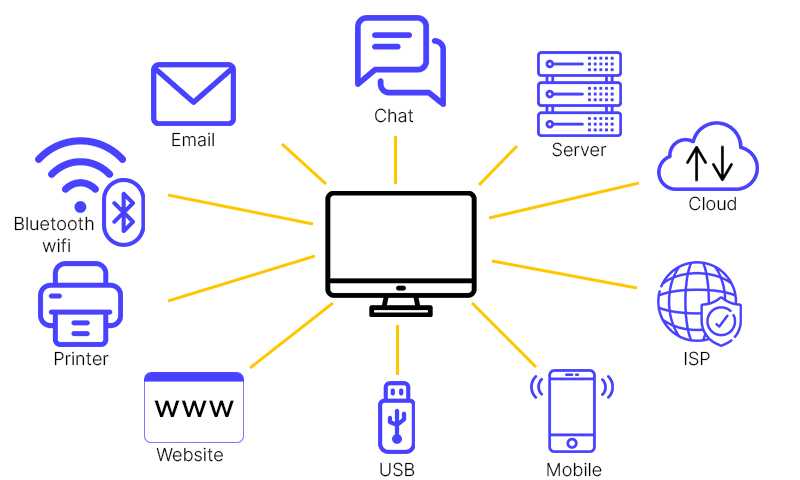
Data Loss Threats
Data exfiltration, or the movement of data without company authorization, is one of the most serious data threats. It is also referred to as data extrusion. Data exfiltration can occur in a variety of ways, including:
- Email and instant messaging are two methods for confidential data to leave the network.
- Without authorization, a user can copy data onto an external hard drive.
- An employee may upload data to a public cloud or can copy data onto an external hard drive which the company has no control.
- An outsider can gain access and steal data through any hacking technique.
- Unintentional or negligent data exposure can also result in breaches. Employees may lack sufficient knowledge of how to handle sensitive data.
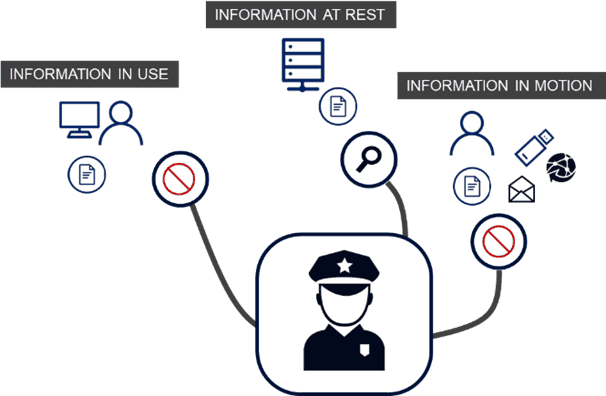
DLP Solution
A holistic DLP solution gives the information security team complete visibility into all data, including:
- Data in Use: This is data that is currently being accessed, processed, updated, or read by a system/user. This includes data stored or processed in databases, CPUs, and RAM. DLP secures data used by an application or endpoint through user authentication and access control.
- Data in Motion: This is data that is actively moving from one location to another, either over the internet, between networks, from a local storage device to the cloud, or via a private network. Because data is frequently less secure while in transit, it is critical to have effective data protection measures in place, such as encryption and/or other e-mail and messaging security measures.
- Data at Rest: This is data that is archived or stored on a device or hard drive and is not actively moving between devices or networks. Data at rest is less vulnerable than data in motion, but it can be a more valuable target for hackers. As a result, it is critical to implement security measures to prevent cybercriminals from gaining access to it, such as access restrictions and user authentication.
Types of DLP Solution
There are three types of DLP:
- Network DLP: DLP for networks monitors and protects all data in use, in motion, or at rest on a company’s network, including the cloud. It monitors and analyzes the network activity and traffic of the organization, including email, messaging, and file transfers/share, to detect when business critical data is sent in violation of the organization’s information security policies.
- Endpoint DLP: monitors all endpoints, such as servers, computers, laptops, mobile phones, and any other device on which data is used, moved, or saved, to prevent data leakage, loss, or misuse.
- Cloud DLP: It is a subset of Network DLP that is specifically designed to protect organizations that store data in cloud repositories.
What kinds of threats does DLP help to stop?
- Internal threats: An insider is anyone who has access to corporate systems. Employees, ex-employees, contractors, and vendors are all examples of this. Insiders who have access to sensitive data may leak, destroy, or steal it. By tracking sensitive information within the network, DLP can help prevent unauthorized forwarding, copying, or destruction of sensitive data.
- External attacks: The ultimate goal of a phishing or malware-based attack is often data exfiltration. External attacks can also result in permanent data loss or destruction, such as when internal data is encrypted and rendered inaccessible in a ransomware attack. DLP can aid in preventing malicious attackers from obtaining or encrypting internal data.
- Accidental data exposure: Insiders frequently inadvertently expose data; for example, an employee may send an email containing sensitive information to an outsider without realizing it. DLP can detect and prevent accidental data exposure in the same way that it can stop insider attacks by tracking sensitive information within the network.
Common features of DLP solutions
- Monitoring: provide visibility into who is accessing data and systems, and from where.
- Filtering: filter data streams to restrict suspicious or unidentified activity.
- Reporting: logging and reports helpful for incident response and auditing.
- Analysis: identify vulnerabilities and suspicious behavior, and provide forensic context to security teams.
How does DLP work?
There are two main technical approaches to DLP:
- Context analysis: It analyzes the metadata or other properties of the document, such as header, size, and format.
- Content awareness: It involves reading and analyzing a document’s content to determine if it contains any sensitive information defined by the company practice and policy.
Modern DLP solutions are a hybrid of the two approaches. DLP examines the context of a document in the first stage to determine whether it can be classified. If the context is insufficient, it uses content awareness to search within the document.
There are several techniques commonly used for content awareness:
- Rule Based: DLP tries to find the sensitive data in the documents based on the detector. For some certain data types, there are already predefined global detectors available such as searching for credit card number or Social Insurance Number etc. Also a custom made detector written in the form of regular expression can be written to identify the same sensitive information based on the pattern.
- Dictionaries: The DLP solution can identify concepts that indicate sensitive information in unstructured data by combining the use of dictionaries, taxonomies, and lexical rules.
- Exact data matching: The solution generates a “data fingerprint” and looks for exact matches in a database dump or currently running database. One disadvantage of this technique is that creating a data dump or accessing live databases can have a negative impact on performance.
- Exact file matching: It hashes the entire file and searches for files that match this hash. This method is very accurate, but problems occur with the files having multiple versions.
- Partial document match: It can identify files where there is a partial match; for example, the same form filled out by different users.
- Statistical analysis: It can use machine learning algorithms for Bayesian analysis to identify content that violates a policy or contains sensitive data. The effectiveness of these techniques can be increased by feeding more labeled data to the algorithm for training.